Math Cheatsheet
Trigonometry
Pi
const float pi = 3.14159265f; // but an infinity of digits in reality
Cosinus & Sinus
 (From http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Geek3 , under GNU Free Documentation License )
(From http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Geek3 , under GNU Free Documentation License )
Unit circle
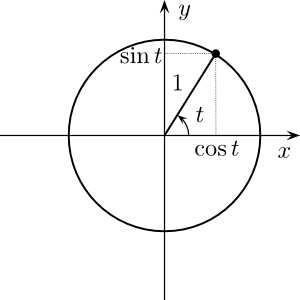
( Modified from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User:Gustavb under Crative Commons 3.0 )t is an angle in radians.
0 radians = 0 degrees
180 degrees = Pi radians
360 degrees ( full circle ) = 2*Pi radians
90 degrees = Pi/2 radians
Vectors
ALWAYS know in which coordinates your vector is. See section 3 for details.
Homogeneous coordinates
A 3D vector is (x,y,z), but a homogeneous 3D vector is (x,y,z,w).
- w=0 : it’s a direction
- w=1 : it’s a position
- else : it may still be correct, but you’d better know what you’re doing.
You can only multiply a 4x4 matrix with a homogeneous vector.
Length
Just like cartesian distance : sqrt( x² + y² + z² ). w doesn’t count.
Cross product
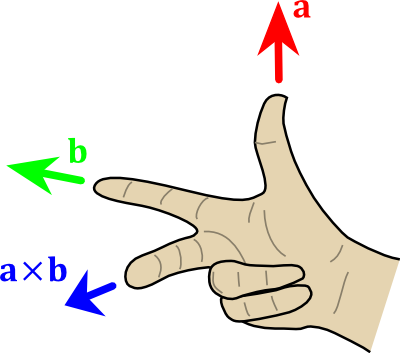
( Modified from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User:Acdx , former image under Creative Commons 3.0 )The X is the notation for the cross product. length( a x b ) == length(a) * length(b) * sin(θ), so you may want to normalize() the result.
Dot product
##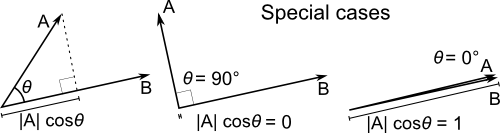
( from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Dot_Product.svg )A.B = length(A)cos(Theta) , but most likely computed as A.xB.x +A.yB.y +A.zB.z
Addition and substraction
compontent-wise :
res.x = A.x + B.x
res.y = A.y + B.y
...
Multiplication
compontent-wise :
res.x = A.x * B.x
res.y = A.y * B.y
...
Normalization
Divide the vector by its length :
normalizedVector = vec * ( 1.0f / vec.length() )
Matrices
Matrix-Matrix multiplication
example for a translation matrix :
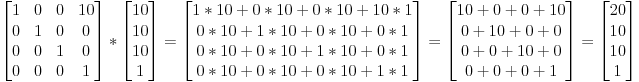
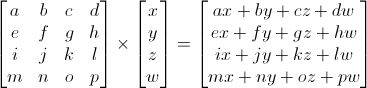
Matrix-Vector multiplication
Usual Transformations
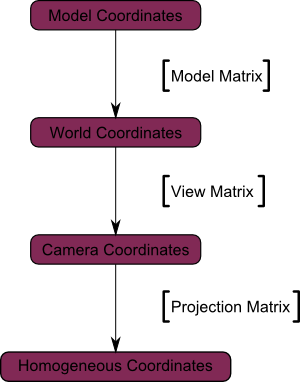
… but in your shaders, you can also represent your vectors in tangent space. And in image-space when you do post-effects.